Main menu
You are here
Model entry
| Search | Simulistics | Model catalogue | Listed by keyword | Listed by ID | Listed by title | Listed by date added |
Drainage pattern
Model : drainage1
Simile version : 4.0
Date added : 2005-02-02
Keywords :
Spatial modelling ;
Fixed-membership submodel ;
Water ;
Description
A classic spatial problem is calculating the drainage pattern for a given land area. If the land is divided in to cells in a grid with the altitude of the land in each cell being known the law the drainage direction for each cell can be found by finding the neighbour with the lowest altitude.
Generally, a procedural algorithm involving program loops is used to find the lowest neighbours. However, in Simile mathematical expressions more often used to specify the relationships between variables. (These expressions are often closer to how one would write up the model in a paper but may feel a little unfamiliar to those who often write programs to solve problems with computers.)
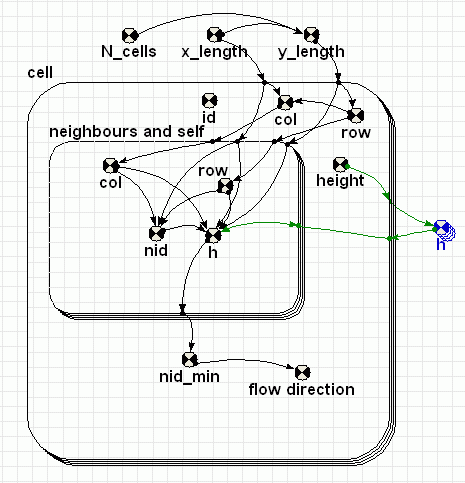
In this Simile model we have a collection of cells numbered 1 to N (the cell's Id) represented by the submodel cell. The cells are arranged in a grid N_cols by N_rows with cell 1,1 being in the lower left and the cell and row of each cell is calculated from its Id
Files
Model fileClick on the icon to download the model file. (You will need Simile to examine and run the model. A free evaluation version is available from the products page.) Some browsers may attempt to display the model file, rather than open it in Simile; in this case, use the browser back button to return to this page, and use the context menu (invoked by right-clicking on the link) to save the target file to disk. |
|
|
|
|
Diagram
Equations
Equations in drainage1 Variable h : Height array h = [height] Where: [height]=cell/height Comments: Outside the cell submodel to provide an array of heights the elements of which are addressable from inside /cell and "/cell/neighbours and self" . (Inside a submodel only values for the current instance is accessible.) Equations in cell Variable col col = index(1)-(row-1)*3 Variable flow direction : Bearing from north to lower neighbour (degrees) flow direction = if nid_min==1 then 225 elseif nid_min==2 then 180 elseif nid_min==3 then 135 elseif nid_min==4 then 270 elseif nid_min==6 then 90 elseif nid_min==7 then 315 elseif nid_min==8 then 0 elseif nid_min==9 then 45 else-1 Comments: -1 if no lower neighbour Variable id id = index(1) Variable nid_min : Neighbour ID of the lowest neighbour nid_min = posleast([h]) Where: [h]=neighbours and self/h Comments: If there is no lower neighbour the value will be the the Neighbour ID of itself, i.e. 5. The Neighbour ID is the index of the "neighbours and self" submodel instances. Variable row row = int((index(1)-1)/3)+1 Equations in neighbours and self Variable col : Column of the cells neighbour's and itself col = col+element([-1,0,1,-1,0,1,-1,0,1],index(1)) Where: col=../col Comments: If the cell is at the edge of the grid some of the "neighbours" will be outside the grid. Variable h : Height of the cell's neighbours and itself h = if col>=1 and col<=3 and row>=1 and row<=3 then element([h],nid)else 1.0E+300 Where: [h]=../../h Comments: Height is assigned the value 1.0E+300 if the "neighbours" will be outside the grid. Variable nid : ID of the cell's neighbours and itself nid = 3*(row-1)+col Comments: If the cell is at the edge of the grid some of the "neighbours" will be outside the grid Variable row : Row of the cells neighbour's and itself row = row+element([-1,-1,-1,0,0,0,1,1,1],index(1)) Where: row=../row Comments: If the cell is at the edge of the grid some of the "neighbours" will be outside the grid.
Results
|
 |
|
Copyright 2003-2024 Simulistics Ltd
